Linux 的 audit 服務是什麼?以前我也不會去注意,直到有一天系統 crash,不知道為什麼,打開 Monitor,只出現一堆這樣的訊息:
audit: audit_backlog=326 > audit_backlog_limit=320
audit: audit_lost=39095317 audit_rate_limit=0 audit_backlog_limit=320
audit: backlog limit exceeded
這也許不是 crash 的主因,但crash引發audit log 淹沒我的記錄寫入才引起我的注意,因此來研究一下 audit。
什麼是 audit
Linux 系統中已經 syslog 了,syslog 會記錄系統狀態、如硬體的警告或應用軟體的記錄等。但是syslog屬於應用層,且僅只於此一應用而已,沒辦法記錄太多資訊,同時也無法確知應用程式是否能正確的寫入,例如因為權限問題無法執行應用程式時,audit可以替我們寫下這些記錄。因此,audit 誕生以彌補 syslog 的不足,也能來記錄1核心層的事件:檔案的讀寫、系統呼叫、權限的狀態、2開啟audit記錄的使用者事件等。並把log寫在下面這個檔案中:
/var/log/audit/audit.log
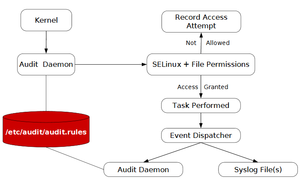
audit 運作的流程
當觸即核心的運作時,audit就會把記錄寫下來,例如開啟 /etc/shadow、觸碰sellinux等等。
(圖片取自參考資料4)
Audit Daemon 運作和一般的daemon 一樣,運作時也得適用selinux的規則。
安裝及啟動
CENTOS7原本就內建有這項服務,可檢查是否有安裝
audit-2.6.5-3.el7_3.1.x86_64
audit-libs-2.6.5-3.el7_3.1.x86_64
安裝/更新
# yum install audit audit-libs
# yum update audit
啟動/停止/重啟
# service auditd stop
# service auditd start
# service auditd restart
查看運作狀態
操作
audit 有三個操作的工具:
ausearch - 用來查詢 audit logs 的工具。
aureport - 產生 audit 系統簡報的工具。
建立監看目錄
# auditctl -w /root
建立監看目錄,給定索引標籤 touch
# auditctl -w /root -k touch
查看已指定監看的目錄
# auditctl -l
移除監看的目錄
移除全部規則和監看
設定每秒最大筆數 20
顯示目前的設定參數和狀態
# auditctl -s
檢查今天檔案及系統的簡報狀態
查看今日的報告
Summary Report
======================
Range of time in logs: 西元2018年04月06日 08:55:33.201 - 西元2018年04月06日 15:09:02.743
Selected time for report: 西元2018年04月06日 08:55:33 - 西元2018年04月06日 15:09:02.743
Number of changes in configuration: 11
Number of changes to accounts, groups, or roles: 0
Number of logins: 1
Number of failed logins: 3850
Number of authentications: 2
Number of failed authentications: 10451
Number of users: 2
Number of terminals: 7
Number of host names: 81
Number of executables: 11
Number of commands: 9
Number of files: 667
Number of AVC's: 28004
Number of MAC events: 1
Number of failed syscalls: 27224
Number of anomaly events: 0
Number of responses to anomaly events: 0
Number of crypto events: 38789
Number of integrity events: 0
Number of virt events: 0
Number of keys: 2
Number of process IDs: 8381
Number of events: 84484
查看主機的活動統計
===========================
total host
===========================
27799 84.46.7.8
13034 46.59.222.82
6329 42.7.26.60
2314 port-1793.pppoe.wtnet.de
1086 port-56731.pppoe.wtnet.de
828 218.29.188.109
679 139.217.15.94
390 103.99.0.120
78 170.210.83.114
55 ?
52 103.99.3.161
44 18.221.91.21
39 202.97.205.78
29 103.207.36.56
27 5.188.10.182
27 181.214.87.4
26 103.207.39.211
25 153.124.169.17
25 95.140.124.171
22 121.18.231.66
22 122.226.181.166
22 221.194.44.211
22 121.18.238.39
查看監看的目錄(或檔案)
只要有讀寫的都會被記錄下來
查看今天的記錄
利用 -ts 指定日期 -hn 指定存取的來源位址
上面代表查詢 2018年4月6日,IP來自46.59.222.82的記錄
-ui 來指定 user name (UID),例如找出 (uid 506) 的操作
讀取具有標籤的監看
# ausearch -i -f /root -k touch
設定檔
audit 的寫入的規則在這個檔案中
/etc/audit/rules.d/audit.rules
寫完規則會建立規則檔 /etc/audit/audit.rules,主要分為三種類別:
- 基本 audit 指令 Basic audit system parameters
- 檔案或目錄監看 File and directory watches
- 系統呼叫 System call audits
1.基本 audit 指令
audit.rules
-D
# buffer大小,預設256,改為8192
-b 8192
# 失敗控制旗標 0:silent, 1:印出錯誤,預設, 2: panic 把系統關閉—非正常關閉,造成資料遺失
# 生失效,0為失效,1為生效(預設)
-e 1
# 每秒建立資料最大筆數20,如不限制可設為0
-r 20
2.,檔案或目錄監看
和前面介紹的 auditctl 參數相同,只是寫在設定檔
-w /home/note -k note
# 觀查檔案 /etc/auditd.conf,-p 設定權限為rxw及a修改等屬性變更
-w /etc/auditd.conf -p rxwa
3.系統呼叫
-a always,exit -F arch=b64 -S adjtimex -S settimeofday -k time_change
-a always,exit -S unlink -S unlinkat -S rename -S renameat -F auid>=500 -F auid!=4294967295 -k delete
-a always,exit -F path=/etc/shadow -F perm=wa
系統呼叫的部分我比較陌生,在官網[5]上有一些範例說得並不是很清楚,留待看倌有需要自己去研究
其他說明
• 目錄觀察的詳細度比檔案觀察低
• 無法使用任何的萬用字元,如?或*
• 只能設定已存在的檔案,若設定觀察目錄而有新增檔案,新檔案只會在下次 audit 重啟後才會加入
參考資料
[1] http://puremonkey2010.blogspot.tw/2014/02/linux-auditctl.html
[2] 檢查誰修改檔的動作 http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-audit-files-to-see-who-made-changes-to-a-file.html
[3] Linux Audit Quick Start SUSE Linux Enterprise 10 SP1 http://www.novell.com/documentation/sled10/pdfdoc/auditqs_sp2/auditqs_sp2.pdf
[4] The Linux Audit Subsystem Deep Dive http://linuxvm.org/present/SHARE113/S9203sw.pdf
重編修原文2010-09-01 11:39:25